/Observed Data/Campaigns
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Update frequencies
status
-

The NourDem project aims to carry out annual trawling cruises in the three estuaries of the Seine, the Loire and the Gironde.
-
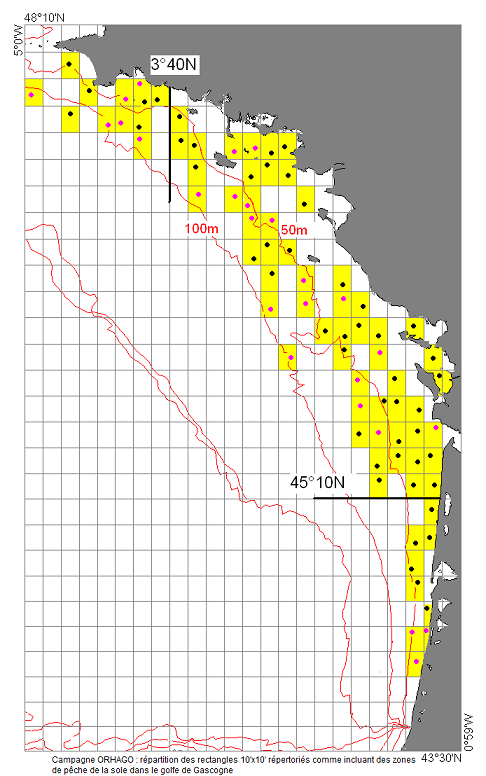
The ORHAGO cruises (Observation of the benthic aquatic resources of the GOlfe de Gascogne) are part of Ifremer's mission of observation and expertise in support of fisheries management. Their main aim is to obtain series of abundance indices for flatfish and in particular for sole. Consequently, the choice was made to adopt a beam trawl to comply with the standards of the International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES) for flatfish. This choice has made it possible to be part of the campaigns coordinated by ICES and thus to be a member of a community in which the methodology and results can be discussed each year in the ICES WGBEAM working groups. Since 2013, the ORHAGO campaigns have been used to assess the state of the Bay of Biscay sole stock. They allow this assessment to be carried out analytically, i.e. using a model to analyse and simulate the dynamics of the stock. The ORHAGO campaigns are also a source of information on the evolution of benthic populations and coastal benthic habitats in the Bay of Biscay.
-
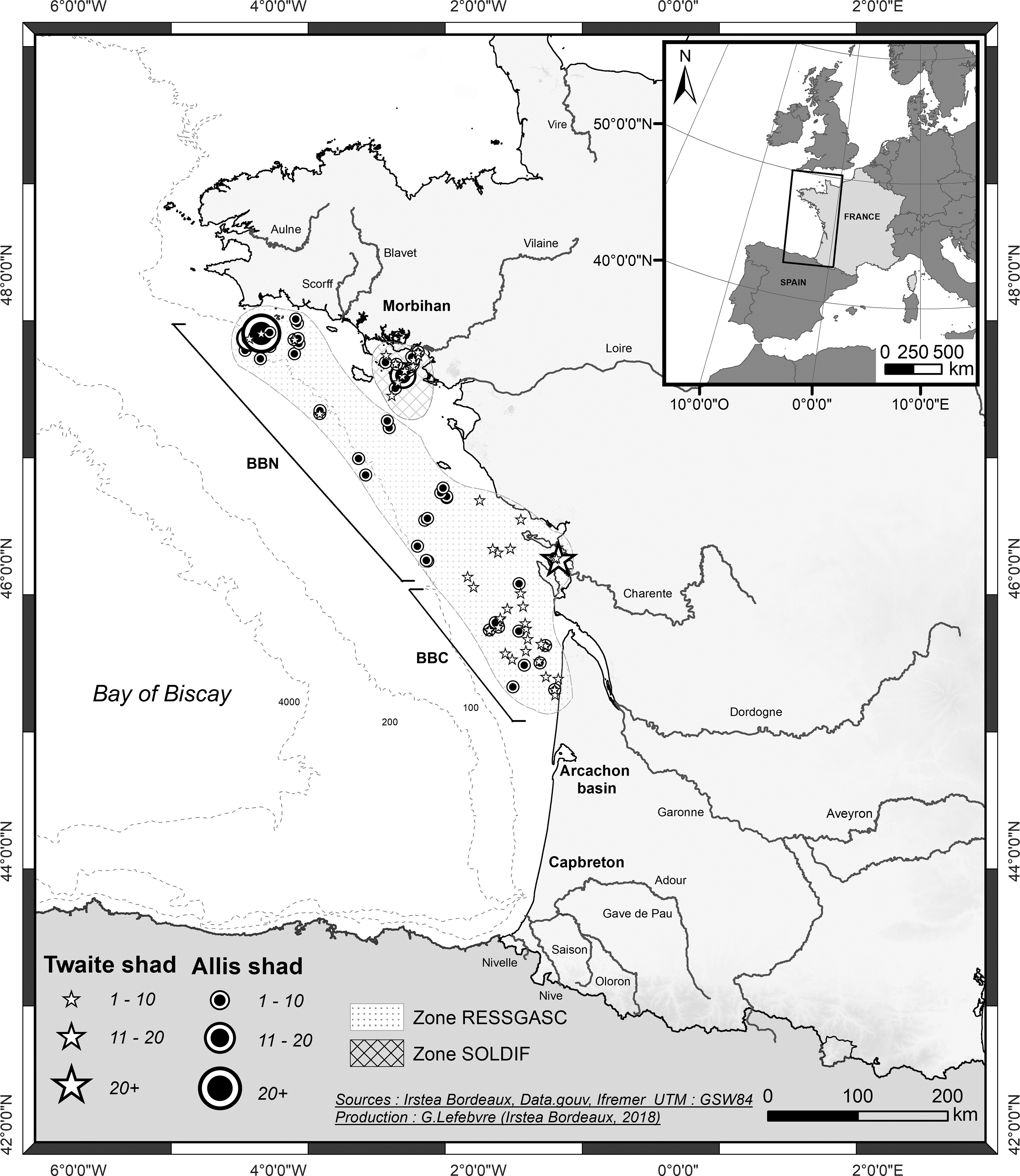
The 62 RESSGASC campaigns allow the quarterly assessment of the quantities of various species (hake, sole, Norway lobster, etc.) discarded by fishing vessels (individuals below legal landing size). This information, together with data collected from the demographic structure of landings (using samples from auctions), is essential for the evolution of commercial fish stocks.
-
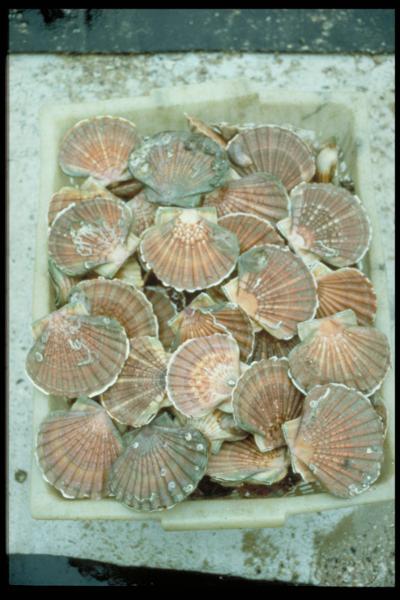

The aim of these cruises, which took place on the Thalia, was to evaluate the abundance of the scallop stock in the Charentais channels.
-

The Bargip project : acquisition of scientific data and knowledge to produce advices on integrated management of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in North-East Atlantic.
-
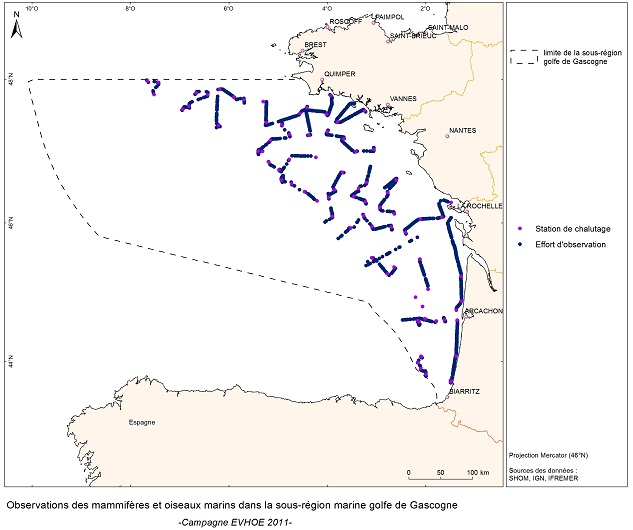
EVRWE is a multiannual survey with the following objectives: - Building up time series of abundance indices for the main dermersal and benthic species in the Celtic Sea and the Bay of Biscay. - Measuring inter-annual changes in their recruitment. - Mapping the spatial distributions of the species and their inter-annual variations, as well as looking for the origin of this variability (biotic and/or abiotic parameters, fisheries impact). - In the framework of the 'Bay of Biscay' challenge, the data collected are vital for understanding changes in faunal communities.
-
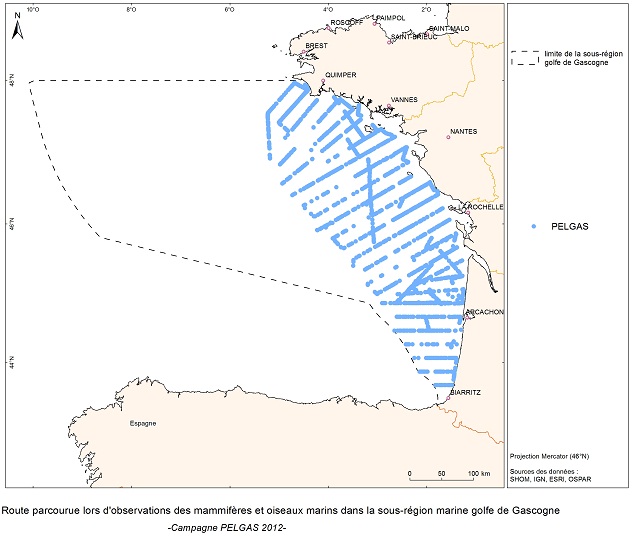
The objective of the PELGAS cruise is to monitor distribution and abundance of pelagic species fished in the Bay of Biscay, using two direct evaluation methods: acoustics and spawning estimates. The cruise was conducted in coordination with France, Spain and Portugal, in the framework of the European council regulations (EC No 1543/2000 of 29 June 2000 and No 1639/2001 of 25 July 2001).
-

Ecological study of coastal nurseries in the Bay of Biscay: abundance and the quality of benthic and demersal fish juveniles (targeted species: common sole, Solea solea L.), biological indicators, relationship with the physical parameters of the habitats (bathymetry, sediments, hydrology) and with associated epibenthic populations (trawls for observing invertebrates).
-

The annual PELMED (PELagiques MEDiterranée) fisheries resource assessment campaign is carried out by the Laboratoire Halieutique Méditerranée of the Ifremer station in Sète. The objectives of these cruises are : 1. Evaluate the biomass of small pelagic fish (anchovies, sardines) by direct method. For this, the campaign must alternate between acoustic prospecting and identification trawling. An acoustic signal is sent from a sounder fixed under the vessel and each time it encounters the bottom or schools of fish, it is reflected and retransmitted to the sounder. In this way, the shape and intensity of these echoes that materialize the schools of fish can be observed continuously. Species identification trawls are carried out in order to define the proportion of species present in the echoes detected. 2. Collecting as many biological parameters as possible on the target species of small pelagics (anchovies, sardines, sprats) to better understand the population dynamics of these species. For this purpose, morphometric measurements, as well as the determination of the sex and maturity stage of the fish are carried out. Finally, otoliths are taken in order to determine the age of the fish. These biological parameters are very important to complete the biomass assessment and have a better understanding of the processes underlying the variability of these populations. This allows for example to determine the age structure or size structure of the populations, to have an idea of their energy reserves, etc. 3. To better understand the pelagic ecosystem as a whole, from plankton to top predators. The primary goal of the PELMED cruise is to evaluate small pelagic stocks, but it also aims to accumulate as much data as possible on the different compartments of the pelagic ecosystem, from physical parameters (temperature, salinity) to top predators (marine mammals, birds), through the different lower trophic levels (phyto- and zooplankton, small pelagic fish). Thus, after each trawling, a hydrological station is carried out with the measurement of temperature and salinity along the water column via a CTD, water and phytoplankton samples with a Niskin bottle and zooplankton samples using a vertical line of WP2. Finally, throughout the campaign we carry out the observation and counting of birds and marine mammals. In addition to the understanding of the ecosystem, this should provide a number of indicators necessary for monitoring the marine environment under the MSFD (Marine Framework Directive).
-

The observation of ecosystems by Ifremer's Fisheries Information System (SIH) is based on a network of sea cruises. It aims to assess the state of stocks of the various species fished in France and Europe. It also enables the characterisation of the marine ecosystem in which the populations evolve. 23 scientific cruises take place each year at sea, enabling data to be collected for more than 30 years for the oldest. Thanks to the use of standardised fishing gear, the data acquired each year on board scientific vessels or professional fishing vessels contribute to the calculation of the index of abundance, with thousands of fish taken during timed trawls. The fish are measured and their age is assessed by measuring their otoliths (small bones located in the inner ear of the fish).
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA